What Is a DNS Cache?
A DNS cache contains all the DNS information on your computer for all the sites that you have visited. Your browser can locate a website more quickly by saving the DNS information locally.
It will first check the local cache for DNS information once you input a website URL. If the directions are located, the DNS cache is used to access the website. The browser will obtain the data from other DNS servers on the internet if it is not already in the local machine.
By doing this, you can be confident that each time you visit a website, your browser will take the quickest path possible to obtain the DNS data it needs to find the website online.
However, if we move our site to another server or change the site domain name, the DNS cache on our computer might still contain the old information. Therefore, when you visit the new site, your browser might not able to locate it by giving you an error or direct you to the old website.
Fortunately, we are able to solve this kind of issue by clearing the cache from our computer. Even thought, the DNS cache will eventually get updated by itself, we still have to wait for a few minutes.
By clearing the cache ourselves, we will be able to update the DNS information instantly. Here’s how we can clear it for each Operating Systems.
What is DNS?
Domain Name System (DNS) is like a phone book for the internet. To access online information, people use domain names like wordpress.com or google.com. The interaction between web browsers is possible through the use of IP addresses.
Each Internet-connected device has a distinct IP address that other computers can use to find the device. DNS servers take the place of the necessity for people to remember IP addresses like 192.168.1.1 (in IPv4) or more complicated modern alphanumeric IP addresses like 2400:cb00:2048:1::c629:d7a2 (in IPv6).
Since every Internet-connected device eg. web servers has its own IP address. The responsibility of the DNS is to convert the domain name into an IP address so that the web browser is able to load Internet resources to or to locate the web server.
Clear the DNS Cache in Windows
First, open the “run” app by hitting the buttons “Windows + R” and type in “cmd”
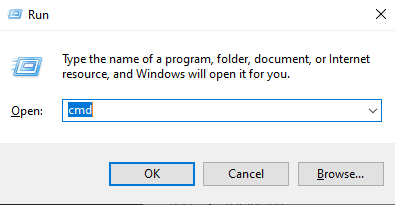
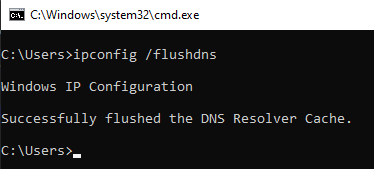
Then, type “ipconfig /flushdns” in the command prompt and hit enter. Your computer will fetch new DNS information now.
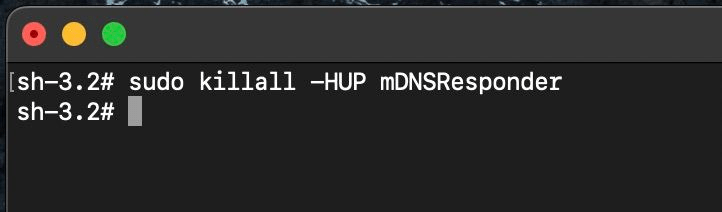
Clear the DNS Cache on macOS
On mac, just open up your terminal and type “sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder”
Another command to clear the cache on MacOS is “sudo dscacheutil -flushcache“
Both these commands should work the same, depending on the MacOS version that you’re using.
Extra tip : If you have change your hosts file content and it is still directing you to the old IP address, using these commands will clear the DNS cache and refresh the hosts file information.
Clear the DNS Cache on Chrome
If you’re using Chrome, clearing the DNS cache on your system might be useless since Chrome itself stores its own DNS cache within the browser.
To clear the cache on Chrome, simply type “chrome://net-internals/#dns” in the address bar.
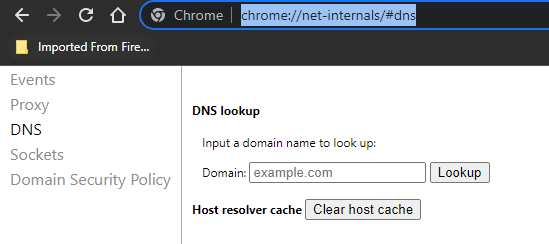
Then, click the “Clear host cache” button.
How to Check for DNS Updates
If you have recently changed your DNS records, switched web host, or started a new website. Your domain will occasionally direct visitors to the new location while other times it will direct them to the old location. Your geographical location and the DNS servers that your browser queries for directions will determine this.
Simply use https://dnschecker.org/ to check if your site is pointing to the right server.
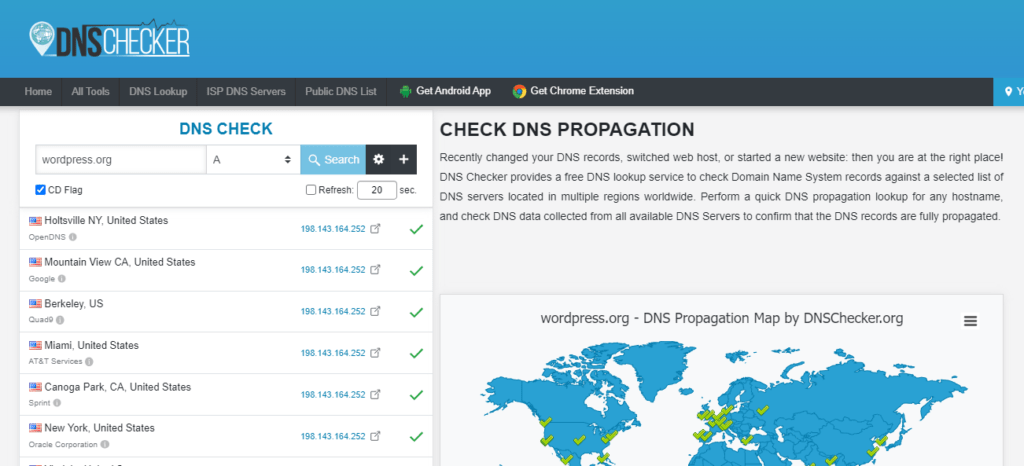
The DNS adjustments you made have now propagated over the internet, if all places show the same IP address with a green checkmark.
Learn how to free up your disk space by cleaning unwanted files here : https://www.kintechie.com/free-up-disk-space-and-clean-unwanted-files/




